How to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for both recreational and professional users. This guide delves into the essential aspects of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and safety procedures to advanced flight techniques and maintenance. We’ll cover everything you need to know to confidently take to the skies, whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to enhance your existing skills.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation.
Understanding drone technology and regulations is paramount for responsible operation, ensuring both your safety and the safety of others.
We’ll explore the intricacies of drone controls, various flight modes, and navigation strategies. We’ll also discuss essential maintenance procedures, troubleshooting common issues, and even delve into advanced techniques for capturing stunning aerial footage. By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and confidence to operate your drone responsibly and achieve exceptional results.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before you even think about taking off, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, understanding relevant regulations, and assessing weather conditions. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and damage.
Drone Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection is essential to identify potential problems before they cause issues in the air. This ensures the safety of both your drone and those around you.
| Component | Check | Pass/Fail | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for cracks, damage, or loose attachment. | Replace damaged propellers immediately. | |
| Motors | Check for smooth rotation and any unusual sounds. | Listen for grinding or unusual noises. | |
| Battery | Ensure the battery is fully charged and securely connected. Check for any damage to the battery casing. | Use only the manufacturer’s recommended battery. | |
| GPS | Confirm a strong GPS signal before takeoff. | Ensure sufficient satellites are acquired. | |
| Camera | Verify camera functionality and lens clarity. | Check for any obstructions or damage. | |
| Gimbal | Ensure the gimbal is functioning correctly and is properly calibrated. | Check for smooth movement and accurate stabilization. | |
| Airframe | Inspect the drone’s body for any damage or cracks. | Pay close attention to areas prone to impact. |
Understanding Local Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local laws and regulations. These regulations often vary by location and are designed to ensure the safety of both the drone operator and the public.
Typical restrictions include no-fly zones near airports, sensitive infrastructure (e.g., power plants, prisons), and crowded areas. Many countries also require drone registration and operator licensing. Always check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations in your area. For example, flying near airports usually requires prior authorization, and flying over people often carries restrictions.
Weather Conditions Checklist
Weather significantly impacts drone operation. Adverse weather conditions can compromise flight stability, damage the drone, and create safety hazards.
- Wind Speed: Check the wind speed. Strong winds can make it difficult to control the drone and can cause it to crash. A general guideline is to avoid flying in winds exceeding 20 mph (32 km/h).
- Precipitation: Rain, snow, or heavy fog can severely affect visibility and damage the drone’s electronics. Avoid flying in these conditions.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect battery performance and drone stability. Operating outside the drone’s recommended temperature range can lead to malfunction.
- Visibility: Ensure good visibility to avoid collisions with obstacles. Low visibility due to fog or darkness can make it difficult to control the drone safely.
Safe Launch and Landing Procedure
- Find a safe, open area away from obstacles and people.
- Perform the pre-flight checklist.
- Power on the remote controller first, followed by the drone.
- Allow the GPS to acquire a signal (usually indicated by a solid GPS indicator light).
- Slowly lift off the drone vertically, maintaining a steady hand.
- During flight, keep the drone within visual line of sight.
- For landing, gently lower the drone vertically to the ground.
- Power off the drone first, followed by the remote controller.
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes
Understanding your drone’s controls and flight modes is paramount for safe and effective operation. Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability, catering to different skill levels and flight scenarios.
Drone Remote Control Functions

- Left Stick: Controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude).
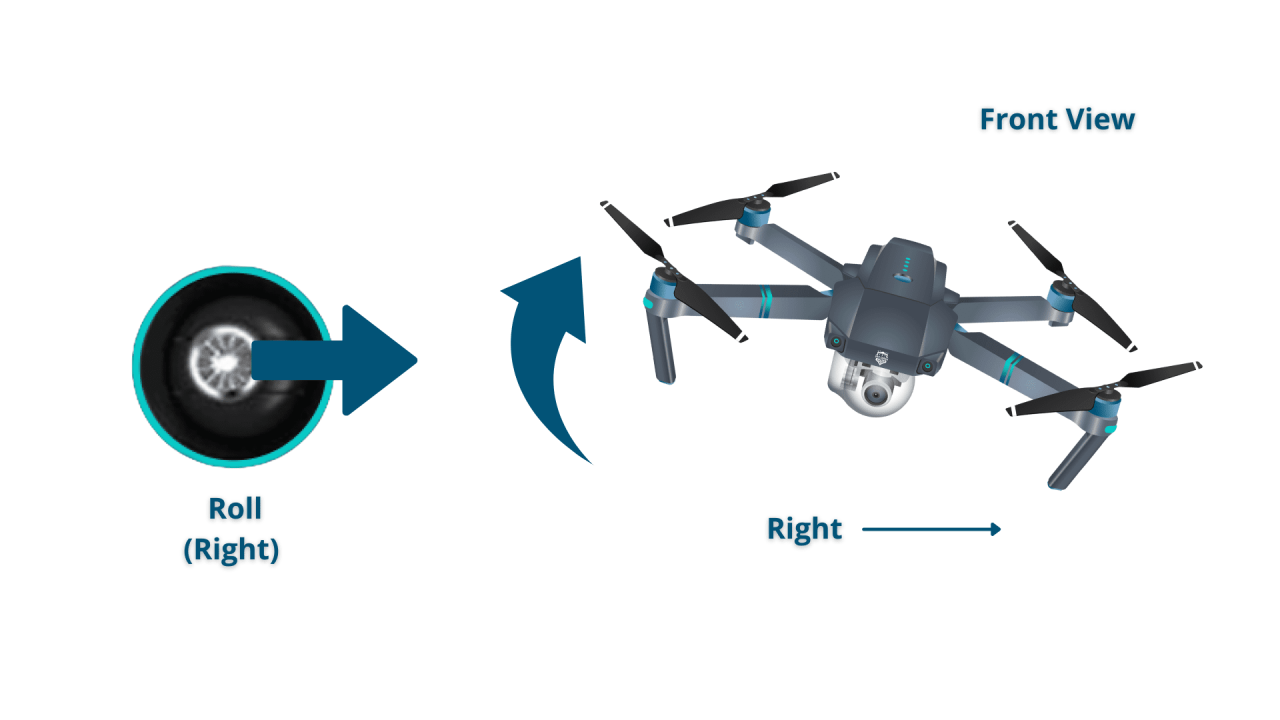
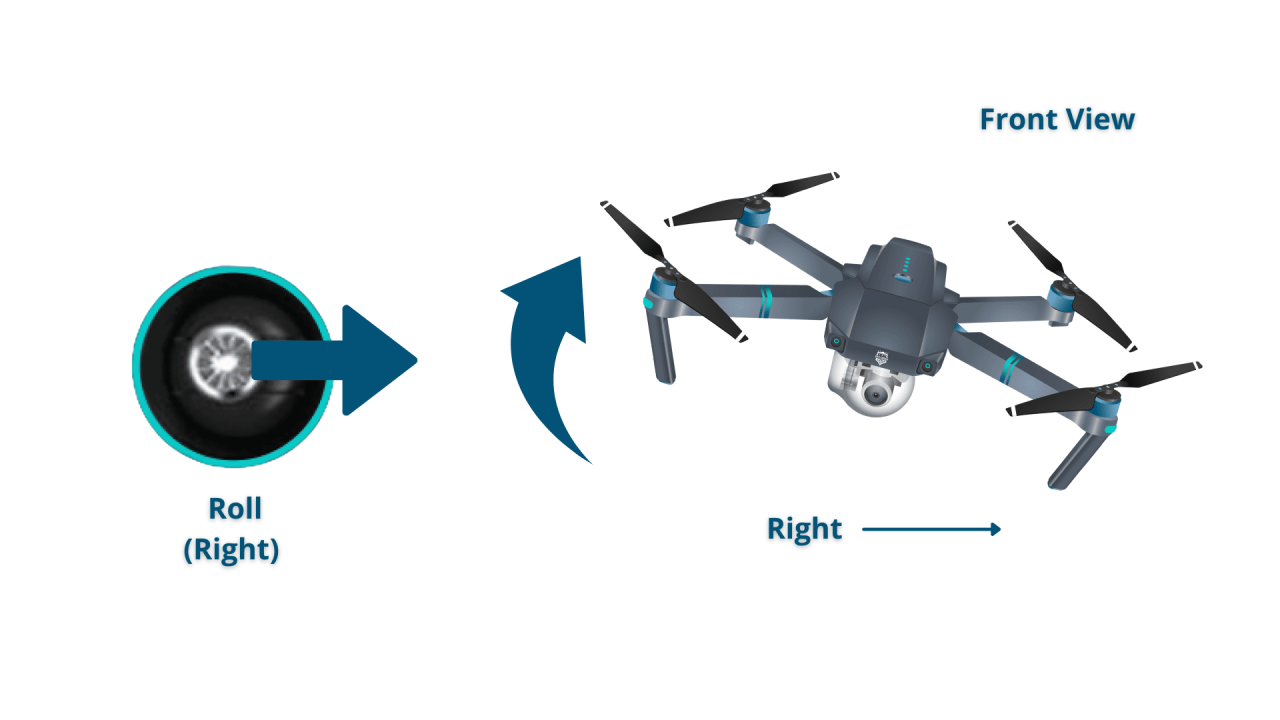
- Right Stick: Controls the drone’s pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right).
- Return-to-Home (RTH) Button: Initiates an automated return to the home point.
- Emergency Stop Button: Immediately cuts power to the motors.
- Camera Control Buttons: Allow adjustments to camera settings (e.g., zoom, photo/video recording).
Flight Modes
Various flight modes offer different levels of control and stability. Choosing the right mode depends on your skill level and the complexity of the flight.
| Flight Mode | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Limits speed and responsiveness for easier control. | Easy to learn, ideal for beginners. | Limited maneuverability, slower flight. |
| Sport Mode | Offers full control and increased responsiveness. | Greater maneuverability, faster flight. | Requires more skill, higher risk of accidents. |
| GPS Mode | Utilizes GPS for position holding and automated features. | Stable hovering, precise positioning, automated functions (RTH). | Requires a strong GPS signal, less effective in GPS-denied environments. |
GPS Assisted Flight Features
GPS-assisted features enhance drone control and safety. These features leverage GPS signals to provide stability, precision, and automated flight capabilities.
- Position Hold: Maintains the drone’s current position and altitude.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point.
- Follow Me Mode: Allows the drone to follow a designated subject.
- Waypoint Navigation: Enables pre-programmed flight paths.
Adjusting Drone Settings
Optimizing drone settings enhances flight performance and image quality. This involves adjusting parameters to suit specific environmental conditions and desired results.
- Camera Settings: Adjust ISO, shutter speed, aperture, and white balance for optimal image capture.
- Flight Parameters: Modify parameters such as maximum speed, acceleration, and responsiveness to suit your flight style and environmental conditions.
Navigating and Operating the Drone
Successfully navigating and operating a drone requires skill, awareness, and strategic planning. Maintaining stable flight, avoiding obstacles, and effectively utilizing the camera are key aspects of proficient drone operation.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning the basics is crucial for safe and effective operation, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone which covers everything from takeoff and landing to advanced maneuvers. Successfully operating a drone requires practice and understanding of the regulations governing its use.
Strategies for Stable Flight and Obstacle Avoidance, How to operate a drone
| Obstacle Type | Strategy | Example | Potential Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trees | Maintain a safe distance, plan flight path carefully. | Fly above tree canopies or around them. | Difficult in dense forests, requires precise maneuvering. |
| Buildings | Avoid flying too close to buildings, respect airspace restrictions. | Plan flight paths that avoid close proximity to structures. | Requires awareness of building heights and proximity. |
| People | Maintain a safe distance, avoid flying over crowds. | Maintain a significant distance from people and crowds. | Difficult in populated areas, requires careful planning. |
| Power Lines | Avoid flying near power lines. | Plan flight paths to avoid any contact with power lines. | Requires careful planning and visual awareness. |
Waypoint Navigation and Automated Flight
Waypoint navigation allows you to pre-program a flight path for your drone, making it ideal for complex or repetitive tasks such as aerial photography or inspections.
Most drones allow you to set waypoints using their dedicated app. You simply mark points on a map within the app, and the drone will autonomously fly between these points. This feature eliminates the need for manual control during the entire flight, allowing the operator to focus on camera work or other tasks.
Effective Use of the Drone’s Camera
The drone’s camera is a key feature, enabling the capture of stunning aerial footage. Effective camera use involves understanding composition, lighting, and camera settings.
- Composition: Use the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques to create visually appealing shots.
- Lighting: Shoot during the golden hour (sunrise and sunset) for soft, warm light.
- Camera Settings: Adjust settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture to optimize image quality.
Common Mistakes and Solutions
- Ignoring wind conditions: Check wind speed before flight. Strong winds can make the drone difficult to control.
- Flying too close to obstacles: Maintain a safe distance from obstacles to avoid collisions.
- Losing sight of the drone: Always keep the drone within visual line of sight.
- Neglecting battery life: Monitor battery level closely and land before it runs out.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are crucial for keeping your drone in optimal condition and extending its lifespan. Proper care prevents malfunctions and ensures safe operation.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
- Daily: Inspect propellers, motors, and airframe for damage. Clean the drone body and camera lens.
- Weekly: Check battery health and perform a calibration check.
- Monthly: Conduct a more thorough inspection of all components, including the gimbal and GPS module.
- Quarterly: Consider a professional inspection if you are not comfortable performing the maintenance yourself.
Battery Care and Charging
Proper battery care is essential for optimal performance and safety. Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow their instructions.
- Storage: Store batteries in a cool, dry place at around 50% charge when not in use for extended periods.
- Charging: Use the manufacturer-recommended charger and avoid overcharging or discharging the batteries.
- Conditioning: Consider occasionally performing a full discharge and recharge cycle to maintain battery health.
Troubleshooting Common Malfunctions
- Low Battery: Land the drone immediately and recharge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Move to an area with a clearer GPS signal or wait for the signal to return.
- Motor Failure: Land the drone safely and contact the manufacturer for support.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Recalibrate the gimbal or contact the manufacturer for support.
Safe Storage and Transportation
Proper storage and transportation protect your drone from damage. Use a protective case or bag and avoid exposing the drone to extreme temperatures or harsh conditions.
- Storage: Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Transportation: Use a hard-shell case or padded bag to protect the drone during transport.
Advanced Drone Techniques and Features
Advanced drone techniques and features unlock greater creative potential and operational capabilities. Mastering these aspects enhances your drone piloting skills and allows you to capture exceptional aerial footage.
Advanced Flight Modes

Many modern drones offer advanced flight modes designed to enhance stability, maneuverability, and creative control. These modes often require a higher level of skill and understanding.
- Cinematic Mode: Provides smooth, slow, and deliberate movements ideal for cinematic shots.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Uses sensors to automatically avoid obstacles during flight.
- Point of Interest (POI): Allows the drone to orbit a specific point, creating dynamic shots.
Drone Software for Video Editing
Various software applications are designed specifically for drone video editing. These tools simplify post-production, allowing you to enhance your footage with professional-looking effects and transitions.
- Adobe Premiere Pro: A powerful video editing software with extensive features for drone footage processing.
- DaVinci Resolve: A professional-grade video editing software offering color grading and visual effects tools.
- Final Cut Pro: Apple’s professional video editing software known for its intuitive interface and powerful features.
High-Quality Aerial Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality aerial footage requires a combination of skill, planning, and technical understanding. This involves mastering camera settings, composition, and flight techniques.
- Lighting: Utilize natural light effectively by shooting during the golden hour or using external lighting.
- Composition: Employ compositional techniques such as the rule of thirds and leading lines to create visually appealing shots.
- Camera Settings: Adjust ISO, shutter speed, and aperture to optimize image quality and reduce noise.
Drone Cameras and Sensors
Different drones utilize various camera and sensor technologies, each with its own strengths and limitations. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right drone for your specific needs.
- Camera Resolution: Higher resolution cameras provide more detail but require more storage space.
- Sensor Size: Larger sensors capture more light, resulting in better image quality in low-light conditions.
- Lens Features: Different lenses offer varying fields of view and focal lengths, influencing the perspective and composition of your shots.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a solid foundation, covering pre-flight checks, control techniques, navigation strategies, and maintenance procedures. Remember that consistent practice and a commitment to safety are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot. By adhering to regulations, prioritizing safety, and continually refining your skills, you can unlock the full potential of your drone and enjoy the thrill of aerial exploration.
Helpful Answers
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and beginner modes are ideal for starting. Look for models with good reviews and ease-of-use features.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, often less in windy conditions.
What happens if I lose GPS signal?
Most drones have return-to-home (RTH) functionality, which automatically guides the drone back to its starting point. However, always maintain visual contact and be prepared to take manual control.
Can I fly my drone in the rain?
No, flying a drone in the rain is extremely dangerous and can cause irreparable damage to the electronics. Always check the weather forecast before flying.